An Introduction to Psychology: Unlocking the Mysteries of the Mind
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Psychology
- The Birth of Psychology
- The Major Schools of Thought
- Behaviorism
- Psychoanalysis
- Humanism
- Cognitive Psychology
- The Science of Behavior and Mental Processes
- The Role of Research in Psychology
- Understanding the Brain and Behavior
- Developmental Psychology: From Birth to Adulthood
- Abnormal Psychology: Exploring Mental Disorders
- Social Psychology: The Power of Social Influence
- Cultural and Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Health Psychology: Mind-Body Connection
- Industrial-Organizational Psychology: Work and Well-being
- Forensic Psychology: Unraveling Criminal Minds
- Sports Psychology: Achieving Peak Performance
- Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of the Human Mind
Introduction to Psychology
Psychology, often dubbed the "science of the mind," is a multifaceted field that delves into the intricacies of human behavior, thoughts, and emotions. This article serves as a comprehensive introduction to the world of psychology, shedding light on its origins, major schools of view, and the diverse areas it encompasses.
The Birth of Psychology
Psychology's journey began in the late 19th century when it emerged as an independent discipline. Previously, questions about human behavior and cognition fell within the realm of philosophy. However, thinkers like Wilhelm Wundt and William James are credited with establishing psychology as a science. Wundt founded the first psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, in 1879, while James penned the seminal work, "Principles of Psychology."
The Major Schools of Thought
Behaviorism
Behaviorism, championed by B.F. Skinner and John B. Watson focus on observable behaviors. It posits that all behavior is learned through interactions with the environment. This school of thought paved the way for studies in conditioning and reinforcement.
Psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud's psychoanalysis delves into the subconscious mind, emphasizing the role of unconscious desires and conflicts in shaping behavior. Freud's work continues to influence modern psychology, particularly in understanding human motivations.
Humanism
Humanistic psychology, led by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers, emphasizes human potential, self-actualization, and personal growth. It celebrates the inherent goodness of individuals and their capacity to strive for self-improvement.
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology explores mental processes such as memory, problem-solving, and decision-making. This school of thought, represented by Jean Piaget and Ulric Neisser, investigates how the mind processes information and makes sense of the world.
The Science of Behavior and Mental Processes
At its core, psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. Researchers employ various methods, including experiments, surveys, and observations, to gather data and draw conclusions about human actions and cognition.
The Role of Research in Psychology
Research plays a pivotal role in advancing psychological knowledge. It allows psychologists to test hypotheses, uncover patterns, and refine theories. Through research, the field evolves and adapts to better understand the human mind.
Understanding the Brain and Behavior
Psychologists delve into the brain's intricate workings to comprehend how it influences behavior. Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and PET scans, enable researchers to explore the connections between brain structure and function.
Developmental Psychology: From Birth to Adulthood
Developmental psychology focuses on the lifespan of individuals, from infancy to old age. It investigates how people grow, learn, and change over time, exploring topics like attachment, identity formation, and aging.
Abnormal Psychology: Exploring Mental Disorders
Abnormal psychology addresses mental disorders, their causes, and treatments. It aims to destigmatize mental health issues and provide support to individuals facing challenges related to their psychological well-being.
Social Psychology: The Power of Social Influence
Social psychology delves into the impact of social interactions on behavior and cognition. It explores topics like conformity, prejudice, and group dynamics, shedding light on how individuals are influenced by their social environment.
Cultural and Cross-Cultural Psychology
Cultural and cross-cultural psychology examines how culture shapes human behavior and cognition. It highlights the diversity of human experiences and the influence of cultural factors on psychological processes.
Health Psychology: Mind-Body Connection
Health psychology explores the connection between mental and physical well-being. It investigates how psychological factors, such as stress and lifestyle choices, affect physical health and vice versa.
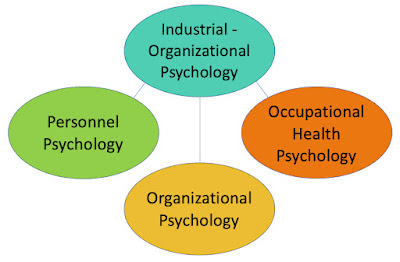
Industrial-Organizational Psychology: Work and Well-being
This branch of psychology focuses on the workplace, addressing issues like job satisfaction, employee motivation, and organizational behavior. It seeks to improve work environments and enhance employee well-being.
Forensic Psychology: Unraveling Criminal Minds
Forensic psychology applies psychological principles to legal contexts. It assists in criminal investigations, profiling, and understanding the motivations behind criminal behavior.
Sports Psychology: Achieving Peak Performance
Sports psychology aids athletes in optimizing their performance through mental training. It explores techniques for managing anxiety, enhancing focus, and building confidence in sports settings.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of the Human Mind
In conclusion, psychology is a multifaceted discipline that seeks to unravel the complexities of the human mind and behavior. From its humble beginnings in philosophy to the diverse array of subfields it encompasses today, psychology continues to captivate the curiosity of those eager to understand what makes us human.
FAQs
1. What is the primary goal of psychology?
The main goal of psychology is to understand and explain human behavior and mental processes. It seeks to uncover the underlying factors that drive our actions and thoughts.
2. Can psychology be applied to everyday life?
Absolutely! Psychology provides valuable insights into decision-making, relationships, and personal well-being, making it highly applicable to everyday life.
3. How do psychologists conduct research?
Psychologists employ various research methods, including experiments, surveys, and observations, to gather data and draw conclusions about human behavior and cognition.
4. Are there cultural differences in psychology?
Yes, cultural factors can significantly influence psychological processes and behaviors. Cultural and cross-cultural psychology explore these differences.
5. What is the significance of abnormal psychology?
Abnormal psychology helps destigmatize mental health issues and provides support and treatment for individuals facing psychological challenges.












Comments
Post a Comment