Key Concepts in Cognitive Psychology
Outline of the Article
Introduction to Cognitive Psychology
Defining cognitive psychologyHistorical overview
Key Concepts in Cognitive Psychology
Perception and attentionMemory processesLanguage and thinking
Theories in Cognitive Psychology
Piaget's stages of cognitive developmentInformation processing theoryConnectionism
Applications of Cognitive Psychology
Educational implicationsCognitive therapiesArtificial intelligence and cognitive modeling
Cognitive Biases and Decision-Making
Types of cognitive biases
Influence on decision-making processes
Neuroscience and Cognitive Psychology
Brain structures involvedCognitive neuroscience research
Challenges and Future Directions
Emerging trendsEthical considerations
Conclusion
Introduction to Cognitive Psychology
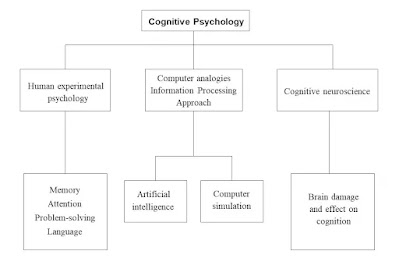
Cognitive psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the study of mental processes such as perception, attention, memory, language, and thinking. It explores how people perceive, think, remember, and learn, shedding light on the complexities of the human mind.
Key Concepts in Cognitive Psychology
Perception and Attention
Perception involves interpreting sensory information, while attention refers to the ability to focus on specific stimuli while ignoring others. Researchers delve into how individuals perceive the world around them and allocate attention.
Memory Processes
Memory encompasses multiple processes like encoding, storing, and retrieving information. Cognitive psychologists investigate these processes and factors influencing memory recall.
Language and Thinking
Understanding language acquisition and the mechanisms behind thought processes form crucial aspects of cognitive psychology. It explores how language shapes cognition and vice versa.
Theories in Cognitive Psychology
Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development
Jean Piaget's theory outlines stages of cognitive development in children, emphasizing how mental processes evolve as individuals grow.
Information Processing Theory
This theory compares the human mind to a computer, focusing on how information is processed, stored, and retrieved.
Connectionism
Connectionist theories explore cognitive processes through interconnected neural networks and their impact on learning and behavior.
Applications of Cognitive Psychology
Educational Implications
Insights from cognitive psychology inform teaching methods, curriculum design, and learning strategies to enhance educational outcomes.
Cognitive Therapies
Therapeutic approaches like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) apply cognitive principles to address mental health issues.
Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Modeling
Cognitive psychology contributes to developing AI systems by mimicking human cognition for problem-solving and decision-making.
Cognitive Biases and Decision-Making
Types of Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases are inherent in human thinking and can affect decision-making processes, leading to errors or irrational judgments.
Influence on Decision-Making Processes
Understanding biases helps in recognizing and mitigating their impact on decision-making in various contexts.
Neuroscience and Cognitive Psychology
Brain Structures Involved
Neuroscientific studies explore how specific brain structures are involved in cognitive processes, linking mental activity to neural mechanisms.
Cognitive Neuroscience Research
Interdisciplinary studies merging cognitive psychology and neuroscience provide insights into brain-behavior relationships.
Challenges and Future Directions
Emerging Trends
Advancements in technology and methodologies are shaping new avenues in cognitive psychology research.
Ethical Considerations
As research evolves, ethical concerns regarding privacy, consent and the use of emerging technologies need addressing.
Conclusion
Cognitive psychology remains integral in unraveling the mysteries of the human mind, impacting various fields from education to mental health and technology. Its continued exploration will shape our understanding of cognition and behavior.
FAQs
1. What is the main focus of cognitive psychology?
Cognitive psychology focuses on understanding mental processes like perception, memory, language, and thinking.
2. How does cognitive psychology impact education?
It influences educational practices by offering insights into effective learning strategies and curriculum design.
3. Can cognitive biases be overcome?
While challenging, awareness and training can help mitigate the impact of cognitive biases on decision-making.
4. What role does cognitive psychology play in AI development?
Cognitive psychology contributes to AI by modeling human cognition for problem-solving and decision-making.
5. Why is ethical consideration crucial in cognitive psychology research?
Ethical considerations are vital to safeguard individuals' rights, and privacy, and ensure the responsible use of technology in research.




Comments
Post a Comment